Photo by Christin Hume on Unsplash
What happens when you type "https://www.google.com" in your browser and press Enter.
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Have you ever wondered what happens when you type the URL "https://www.google.com" in your browser and press Enter? Well, let me explain it to you in simple terms.
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is a web address that you can type into a web browser like Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox to visit a website. It is like the address of a house or a building. For example, if you want to visit Google's website, you will type "https://www.google.com" into the address bar of your web browser, and it will take you to Google's homepage.
Several processes happen behind the scenes to enable you to access the Google website when you type "https://www.google.com" into your browser and hit enter.
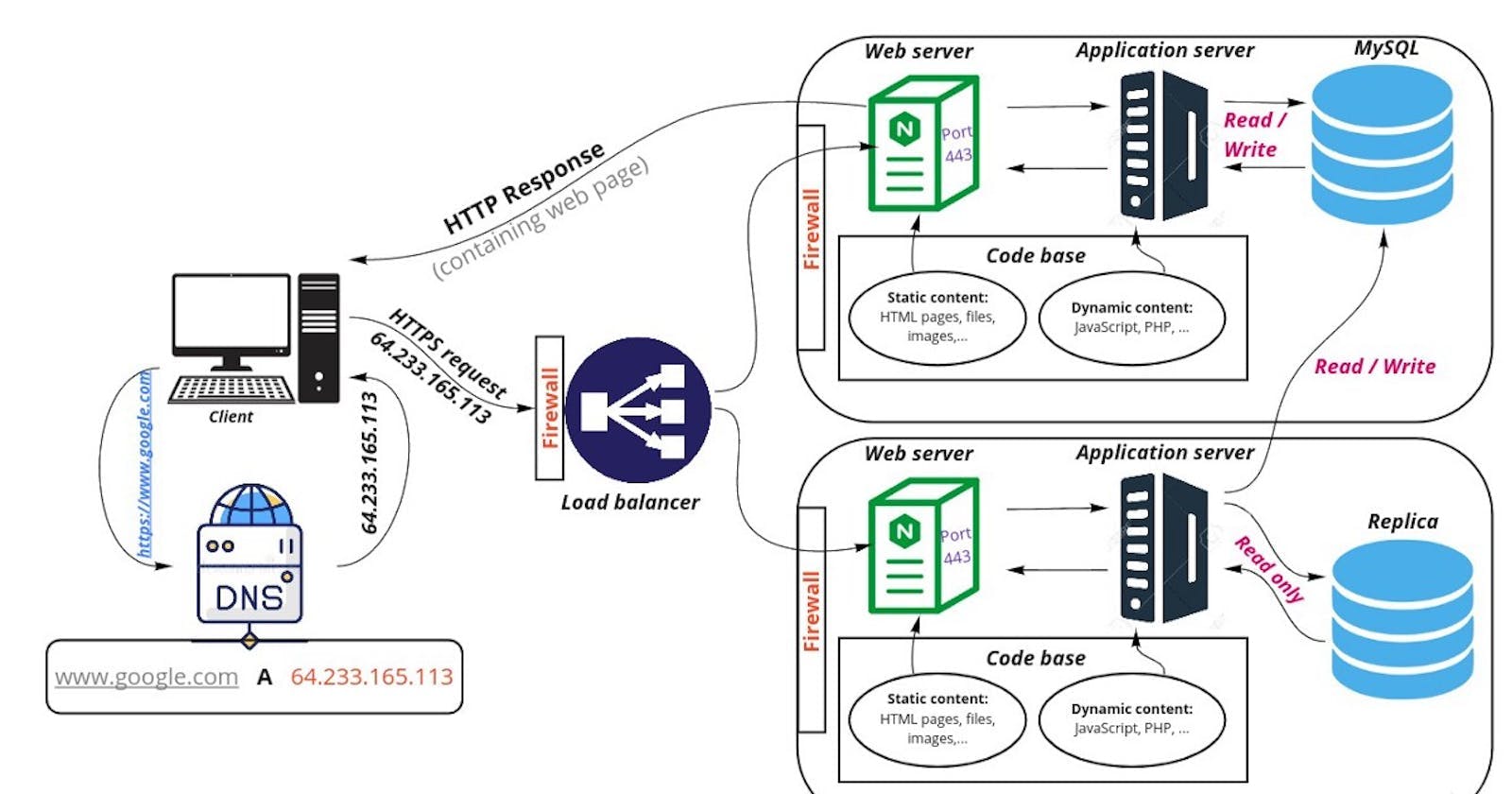
The process starts with your computer sending a Domain Name System (DNS) request to a specialized server, which converts the domain name "www.google.com" into an IP address that looks like this: "64.223.165.113."
An IP address is a unique identifier or special number that instructs your computer where to find a website on the internet. Once your computer has the IP address for the Google website, it sends a TCP/IP request to that address.
The Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) tells the server that hosts the Google website to deliver a copy of the website's files to your computer so that your browser may view them.
Before the files are sent, they need to pass through a firewall, which is a security measure that helps protect against unauthorized access to the server. A firewall is a software or hardware-based security system that checks to make sure that the incoming request is safe, secure, and not harmful.
After the request has gone through the firewall, it's encrypted using Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) or Secure Socket Layer (SSL). This means that the data being sent back and forth between your computer and the web server is secured and can't be intercepted by anyone who might be trying to spy on your internet activity.
Secure Sockets Layer is a technology used to encrypt and protect data as it travels between a web server and a user's web browser. Think of it like a secret code that only you and the other computer can understand. It is commonly used on websites that require secure online transactions, such as online banking, e-commerce websites, and other websites that handle sensitive data.
When the request arrives at the server, it will first pass through a load balancer, which helps distribute the request among multiple servers in a data centre to ensure that the website can handle a large volume of traffic.
A load balancer is used to divide the request among various servers in a data centre before it reaches the server, ensuring that the website can handle heavy traffic. They are designed to improve the performance, availability, and reliability of computer applications and websites by managing the traffic load and preventing any single server or resource from becoming overloaded.
The server hosting of the website is typically made up of several layers, including a web server, an application server, and a database.
The web server is responsible for displaying the actual website files in your browser. It is responsible for serving web pages or other content to clients. When a user requests a web page or resource from a website, the request is sent to the website's web server, which then responds by sending the requested content to the user's web browser.
The application server is responsible for running any code that's needed to dynamically generate parts of the website that help people do things like send emails, use social media, or play games online. An application server is like a chef in a restaurant that provides the resources and tools that help applications run smoothly, just like a chef prepares meals for customers using their kitchen tools and ingredients.
While the database is responsible for storing and retrieving the data that the website needs to function properly, Think of it like a collection of cards in a library, where each card has information about a book such as a title, author, and summary. Databases can be accessed and manipulated using specialized software called database management systems (DBMS). These systems allow users to query, update, and manage the data stored in the database and provide tools for ensuring the security, reliability, and availability of the data. The most common are relational databases and NoSQL or MySQL query languages.
Once the server has gathered all the necessary files and data, it sends them back to your browser, which then displays the Google website on your screen.
So, there you have it! That's what happens when you type in "https://www.google.com" in your browser and press enter. Although it may seem like a lot, the process occurs very swiftly.
To summarize this process visually, the diagram below describes the whole process.